Tuya NB-IoT Common Solution?
Narrow Band Internet of Things (NB-IoT) is built in a cellular mobile communication network to realize thing-to-thing communication and thing-to-person communication. NB-IoT focuses on the low-power wide-area (LPWA) Internet of Things (IoT) market and is an emerging technology that can be widely used around the world.
NB-IoT network consumes only about 180 kHz bandwidth and uses the licensed band. It can coexist with the existing network in three deployment modes, including in-band, protection band, or independent carrier wave. NB-IoT network can be directly deployed in a GSM network, a UMTS network, or an LTE network to reduce the deployment cost and realize a smooth upgrade.
NB-IoT features
- Low power consumptionThe installation environment of IoT applications, such as intelligent meter reading, environmental monitoring, and intelligent agriculture, has no power supply and requires batteries. In order to meet the requirement of 5 to 10 years of battery life, the introduction of PSM and eDRX technology to the NB-IoT network greatly reduces the terminal power consumption. The device is in extremely low power consumption status during most of the life cycle, thus ensuring the service life of the battery.
- Low costNB-IoT terminal adopts narrow-band technology with a less complex baseband. It only uses a single antenna, adopts half-duplex mode, and low-cost RF modules. Most unnecessary functions, such as SRVCC, IMS, emergency call, and other functions, can be cut. At the same time, the SoC built-in power amplifier (PA) is adopted, so that the requirements for the terminal flash storage space, terminal size, and terminal radiofrequency are reduced. The terminal cost of the NB-IoT is greatly reduced.
- Large connectionNB-IoT has 50 to 100 times higher uplink capacity improvement (specific service model) than 2G, 3G, and 4G. NB-IoT provides 50 to 100 times of access compared with existing wireless technology. A single community can support 50,000 users.
- Broad signal coverageWith 164 dB maximum coupling loss (MCL), NB-IoT improves 20 dB gain compared with GPRS. NB-IoT provides better coverage in underground garages, basements, underground pipelines, and other places where signals are difficult to reach.
| Feature | NB technical feature | Value range |
|---|---|---|
| Small amount of data | Limited air interface resources (180 kHz), suitable for small data communication | 50 bytes to 200 bytes is appropriate, the smaller the better |
| Low frequency, long period | Most terminals should be in hibernation status for a long time, with a low frequency of reporting data | Report on a daily basis, and 1 to 2 times a day is appropriate. High-frequency reporting (such as every 30 minutes) occupies a large amount of network capacity. The higher the reporting frequency, the greater the impact on network capacity. |
| Low power consumption | PSM mode of NB network has the lowest power consumption | The first-choice for applications that are sensitive to power consumption |
| Low mobility | NB is suitable for slow movement | Moving speed is less than 30 km/h |
| Deep coverage | NB coverage capacity is relatively good | Support scene coverage such as basement |
| Low rate | The theoretical upstream peak rate is 15.6 Kbit/s and the theoretical downstream peak rate is 21.25 Kbit/s | Large-rate bandwidth type service cannot be carried by NB |
NB-IoT network architecture
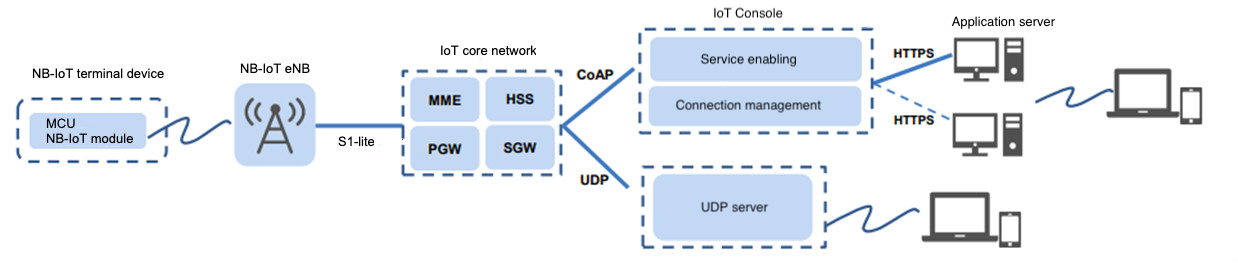
NB-IoT network consists of NB-IoT terminal, NB-IoT base station, NB-IoT Packet Core Network, IoT connection management platform, and industry application server. The access network architecture of NB-IoT is the same as that of LTE.
NB-IoT power-saving mode
The development of the NB-IoT service scale is closely related to the carrier service model. Its applicable scene is the applications with “small traffic, mainly reporting, long-term hibernation, sensitiveness to power consumption, and low mobility”. In order to carry a large number of low-power devices in the NB-IoT network, the most important technologies are PSM and eDRX.
NB-IoT supports three power saving modes: PSM (power saving mode), DRX (discontinuous reception mode), and eDRX(extended discontinuous reception mode).
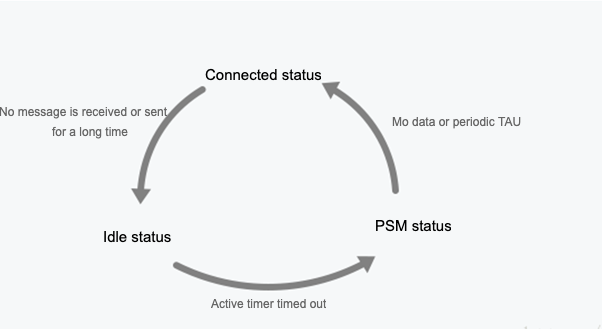
- PSM modeThe terminal is in deep hibernation during the non-service period and does not receive downstream data. Only when the terminal actively sends mobile original data (MO data), the downstream data cached by the IoT Console can be received.In this status, the radio frequency of the terminal is turned off, which is equivalent to a shutdown status. However, the core network side still retains the user context, and the user does not need to attach PDN establishment when entering the idle status or connected status.It is suitable for services without delay requirement on downstream data. A terminal device has low power consumption and adopts battery power supply mode, such as meter reading service.
- Active: the module is active, all functions are normally available, and data can be sent and received. In this mode, the module can switch to the idle mode or PSM mode.
- Idle: the module is in the light sleep status and network connection status, and can receive paging messages. In this mode, the module can switch to the active mode or PSM mode.
- PSM: the module is in the deep sleep status, and only RTC works. The module is disconnected from the network, and cannot receive paging messages. When the timer times out, the module is woken up. The module can also be woken up by pulling down the PSM_EINT pin.
- eDRX modeThe terminal device takes into account the services with low power consumption and certain delay requirements. In each eDRX cycle, the terminal can receive downstream data only in the set paging time window. The terminal is in hibernation status for the rest of the time and does not receive downstream data. This mode can strike a balance between downstream traffic delay and power consumption, such as remotely shutting down gas supply.
 In each eDRX period, there is a paging time window (PTW). The terminal monitors the paging channel according to the DRX cycle, in order to receive downstream data. DRX cycle time is short, and it can be considered that the terminal does not hibernate and can be reached all the time. The terminal is in a hibernation status for the rest of the time. In the eDRX mode, the terminal device is accessible at any time, but the delay is longer depending on the eDRX cycle configuration. This mode can strike a balance between low power consumption and delay.
In each eDRX period, there is a paging time window (PTW). The terminal monitors the paging channel according to the DRX cycle, in order to receive downstream data. DRX cycle time is short, and it can be considered that the terminal does not hibernate and can be reached all the time. The terminal is in a hibernation status for the rest of the time. In the eDRX mode, the terminal device is accessible at any time, but the delay is longer depending on the eDRX cycle configuration. This mode can strike a balance between low power consumption and delay. - DRX modeIt can be considered that the downstream service can reach the terminal device at any time. In each DRX cycle, the terminal detects whether the downstream service arrives. This mode is suitable for the service with high requirements for the delay. Terminal devices generally adopt power supply, such as street lamp service.
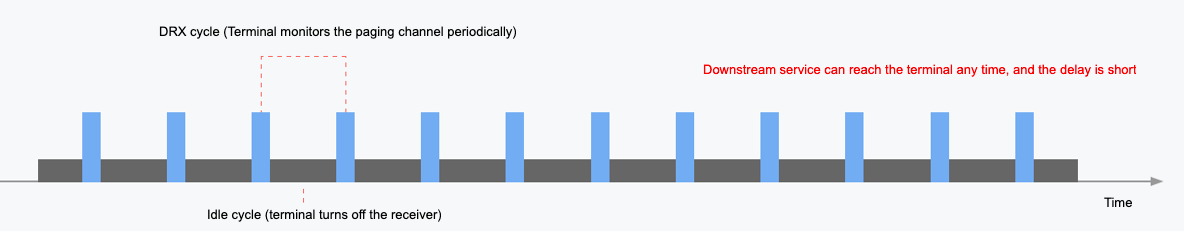 The DRX cycle is short, 1.28, 2.56, 5.12, or 10.24 seconds. The DRX cycle is determined by the operator’s network settings — handling APN service with a SIM card. It can be considered that the downstream service can be reached at any time with a small delay. It is suitable for services with high requirements for the delay, but the power consumption is relatively high. The terminal device generally is powered by mains electricity.
The DRX cycle is short, 1.28, 2.56, 5.12, or 10.24 seconds. The DRX cycle is determined by the operator’s network settings — handling APN service with a SIM card. It can be considered that the downstream service can be reached at any time with a small delay. It is suitable for services with high requirements for the delay, but the power consumption is relatively high. The terminal device generally is powered by mains electricity.
NB-IoT delay
First network access delay: after the NB terminal is powered on, the terminal and the network have lots of message interactions, including authentication, channel establishment, and IP address allocation. It takes 6 to 8 seconds to complete the network access, and obtain the IP address for later data transmission.
Data reporting and receiving delay: after the NB terminal is successfully accessed, when the terminal has data transmission, the terminal will actively establish a wireless connection with the base station. At this time, authentication, IP address allocation, and other processes are no longer required. After the wireless link is successfully established, the data will be sent immediately. The delay of data reporting by the terminal is closely related to the status of the terminal and the wireless network coverage.
| Terminal reports data | Platform sends data (PSM) | Platform sends data (DRX) | Platform sends data (eDRX) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air interface delay + delay between private network and client server | Air interface delay + delay between private network and platform + maximum PSM hibernation cycle (maximum 310 hours) | Air interface delay (750 ms) + DRX paging cycle (maximum 10.24 seconds, minimum 1.28 seconds) | Air interface delay (750 ms) + eDRX paging cycle (maximum 2.92 hours, minimum 5.12 seconds) |
| Second level (3 seconds to 30 seconds) | Hour/day level, depending on terminal reporting cycle | Second level, depending on DRX paging cycle | Second to hour level depending on the eDRX paging cycle |
Key parameters of NB-IoT service acceptance
From the above, it can be seen that the low-power consumption mechanism of the NB application is inseparable from the configuration of SIM card operators. Therefore, when purchasing a SIM card, make clear the APN service you handle. Different APNs are suitable for different application scenes.
Consult Tuya staff when you do not know how to choose APN service.
NB-IoT power consumption
| Terminal status | Power consumption | Measured results of an environment |
|---|---|---|
| PSM status | 3 uA | 2.7 uA |
| eDRX idle status | xxuA to 2 mA | 1 mA |
| DRX idle status | 1 to 4 mA | 1 mA |
| Connection status | Sends 200 mA, and receives 65 mA | Sends 189 mA, and receives 161 mA |